Lean Manufacturing & Six Sigma
Lean Manufacturing and Six Sigma are the most powerful methods to improve the productivity at any process
sábado, 9 de marzo de 2019
sábado, 25 de febrero de 2017
Lean Office - Process Map Before and After
There are many ways to document a Process Map of transactional processes, however I believe that photos and videos represent more clearly the reality.
These two videos are a good example of how to detect areas of opportunity and how to solve them.
The distinction between value-added activities and non-value-added activities can be clearly seen.
And it is an example of how IT can help us with a practical solution.
I hope to help you in your next kaizen event.
Before.
After.
Greetings.
These two videos are a good example of how to detect areas of opportunity and how to solve them.
The distinction between value-added activities and non-value-added activities can be clearly seen.
And it is an example of how IT can help us with a practical solution.
I hope to help you in your next kaizen event.
Before.
After.
Greetings.
jueves, 23 de febrero de 2017
Lean Supply Chain ; Kaizen at Shipping
At Lean Supply Chain Kaizen events, sometimes members of the shipping area teams need ideas on how to streamline activities, some ideas are presented in the following videos.
On this video the team can see the easy way to Strapping.
There are some other ways .....
Some projects are looking for an automated solution and work on one pallet flow....
I never recommend buying anything because Kaizen always seeks to make the improvements with "no money", but in case the ROI can justify it, I think they can be good examples.
There are many benefits, in cost, reduced cycle time, Ergonomics benefits etc.
I hope it's useful.
Continue with the effort in the implementation of Lean supply chain.
On this video the team can see the easy way to Strapping.
There are some other ways .....
Some projects are looking for an automated solution and work on one pallet flow....
I never recommend buying anything because Kaizen always seeks to make the improvements with "no money", but in case the ROI can justify it, I think they can be good examples.
There are many benefits, in cost, reduced cycle time, Ergonomics benefits etc.
I hope it's useful.
Continue with the effort in the implementation of Lean supply chain.
jueves, 1 de diciembre de 2016
Kamishibai 紙芝居; Leadership Process Audit
The use of a visual
tool for auditing standards implemented in Genba or even after a Kaizen event
is extremely important.
Leadership Process auditing using
Kamishibai boards is one of the easiest and most effective.
Although, there is no
standard (which is good since you should always adjust to the organization and
industry where you work) these are some things to consider.
- 1. Create a calendar of visits to the genba is recommended on a weekly basis.
- 2. Create a list of leaders or those responsible for conducting the audit.
- 3. Identify areas where the audit should be done, usually a letter or a nomenclature is placed in the Kamishibai card.
- 4. Kamishibai cards are basically; a compendium of points, to be verified in the areas that correspond. In other words, 5's, VSM, Standard Work, Pull System and mainly 8 wastes. Other special points can be added.
- 5. You should consider another signal (format or card) where the abnormality is written, in order to annex it to the Kamishibai, so that the person in charge of the area can correct this abnormality and there is evidence of it. (Normally this correction becomes Kaizen Blitz)
The discipline and
involvement of the leaders responsible for conducting this audit is
indispensable and mandatory.
In fact in many LMT in
the part of Management Involvement (Culture) is a very relevant point, since it
says much of the discipline.
Attached an excellent
video, where in a few minutes give a very detailed explanation, also offer to
share formats to be modified, to the needs of your organization.
Especial thanks to Kevin Potts for Share this video.
martes, 29 de noviembre de 2016
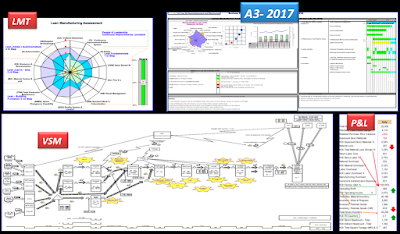
Lean Deployment Plan - (A3-VSM-LMT and P&L)
In preparation for
2017, many companies are developing their Lean and Kaizen Plan.
I will now describe
the mechanism in general for that purpose.
First: The present and future VSM must be created (however
in companies that have already started, they should update the present VSM and
check if the future VSM will meet its objectives). Identify the areas of
opportunity and kaizen that are going to be realized. I strongly recommend that
all VS be reviewed.
Second: Update, (based on the current VSM), the LMT Lean
Maturity Tracker, which is the way, as many companies measure their progress in
Lean.
Third: Review progress based on P & L and Cash
Flow sheet; basically this is how to measure the effectiveness of Lean
activities. Identifying the areas of opportunity, these should be compared,
with opportunities for improvement in the VSM and obviously should be in sync,
in case they are not should review the VSM again and find ways to improve.
Fourth: Update or create the strategic A3, for 2017,
where the LMT, the Gap between VSM present - future, last year's reflection
(which, went well and went wrong) and the Kaizen Plan with date and owners,
Must be reflected. My personal advice is that in that plan we consider a Kaizen
event at least a month, continuity and practice makes it all the difference.
This mechanism applies
in both cases, whether you are about to start with Lean or are in the process,
the path of continuous improvement never ends.
I hope I have
summarized this article in a way that can be easily understood. And mainly, to
be of help and / or guide in its preparation for 2017.
miércoles, 26 de octubre de 2016
Zero Defects – Increasing the Troubleshooting Technique on PCBA’s and Electronics Devises.
In kaizen events it is
very common to be confused in the main objective of Zero Defects. Many people
focus more on how to fill out the forms from their computer and desktop. The formats
such as Ishikawa, 5 whys, 8D and others; don’t need to be filling out just as
requirement.
Obviously formats
helps a lot, however, the most important from my point of view and based on my
own experience it is to understand Sangen Shugi,
Genba.
Genbutsu.
Genjitsu.
The consultant in this
case should guide the team to touch the product and go discarding possible
causes or failure modes that may cause the defect, step by step, until they
find the root cause.
The team therefore
should be documenting the formats with real information, and this must be
handwritten in Genba, with the Real Product with Real Data.
In these examples, you
can see how the teams actually inquired, finding, which is outside the standard
within the product, drawing and taking pictures of the search process and
discard the evidence one to one to be completely convinced. And if possible
many teams have also duplicated the defects to understand in more detail the
phenomenon of the failure.
After all this process the teams goes to document on electronic the findings to have a proper document and evidence of Problem Solving.
In the videos below
are examples of how to perfect methods of finding the problems (Troubleshooting
Techniques) and I think it is a good practice to take a video of our own
method.
Many examples are
described here, for many it sound obvious but possibly for others it could help
especially in the PCBA's and other electronic devices.
I hope this information can help you in your next Kaizen Event.
miércoles, 30 de septiembre de 2015
Tsurube System ( よくバケツ ) – Pull System (JIT)
Many people call Tsurube as system, however, from my point of view and based on my
experience in Japanese companies, is a Method
into the Pull System (JIT). Tsurube combines FIFO (First In First Out) with Kanban,
promoting, sequencing and the correct leveling of inventories at the same time.
Tsurube is the Japanese word for “well bucket”.
As I have commented, it is a method of the pull system, a material replenishment
method used when there is the middle process step is physically separated from
the upstream and downstream processes by lead-time due to distance and/or batch
processing. A “bucket” (container of unprocessed material) is sent down the
“well” (the remote process) and at the same time a full “bucket” (processed
parts) is returned up from the well.
Tsurube is not easy to implement because it requires a
very good quality in processes and a good up time of the machine, since any
interruption or variation breaks the FIFO sequencing.
However many companies require this method or in
other words must implement immediately, hence the importance of having someone
with extensive experience in the implementation.
This
Tsurube method, is used to maintain
a continuous flow when there are interruptions such as process off-line or
off-site and must have a batch system.
Used when the product leaves the production cell
lines or because the process, can not, be in the cell (Kilns, painting, heat
treatments, anodizing, plating, ect) and operates as follows.
A supermarket finished products located at the
end of the line, which has predetermined quantity of material, usually a PITCH,
in this example it will be 30 minutes.
Once the amount is removed; then a kanban signal
its send to the process A, which can be the pacemaker; which prompts you to
start producing parts (quantity = pitch) is sent.
Usually the FIFO system is used to move the
product to process B. Process B also, have and process the same quantity and
this is passed to the process that we have offline. (Process C)
And this last process the same amount to the
process C is passed to end the cycle Process D and then to SMKT Finish Goods;
ant his process is repeated as often as needed.
It is very important to consider the SWIP (Standard Work In Process) the usual way to
calculate is the following.
SWIP = [Total Lead Time =(Transportation Lead
Time + Manufacturing Lean Time)] / Takt Time.
The SWIP (two buckets) maintains continuous flow
through a batch or outside process. Transportation of materials is never empty
in either direction and the arrival of the bucket to the well process is a
signal to produce. It is in effect an instance of a non-card type production
instruction kanban ; it is a FIFO process sequencing.
There are three golden rules for this Tsurube
method:
1.- Respect the FIFO sequence
2.- Quantity shipped must equal amount received
3.- Do not send more parts if those sent were
not received.
Zero Defects and TPM must be implemented before
or at same time (in parallel).
I hope this information will be helpful in your
next kaizen event.
Etiquetas:
Just In Time,
Pull System,
Tsurube,
VSM
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)